Spanish Painting from XIV to XVIII Centuries
From the Renaissance to the birth of the Romanticism movement, these five centuries saw a lot of change in not only the style of paintings, but also the purpose of paintings. By the end of this five century period, Spanish painters were moving towards painting their feelings with more emotion and freedom than had been accepted in early periods.
There can be no doubt that some of Spain's most famous paintings arose out of these styles. El Greco, Goya, Velázquez all made their marks on Spanish art history during this period, and they helped shape the art of centuries to come.
Renaissance Spanish Painting

The Renaissance was a time of great change as well as great artwork and paintings. It lasted for around three centuries from the 14th Century up until the 17th Century. Although the artistic focus was mainly on Italy, Spain also had its fair share of Renaissance painters.
Paintings from the Renaissance period reflect the innovation that was happening in the world at that time, such as the advances in science and technology. The development of the easel meant that painters had their own medium with which to work and were therefore no longer tied to architects for spaces to paint. The 15th and 16th Centuries saw the rise in popularity of the more portable panel paintings, which could be hung and moved around the house with ease.
The High Renaissance period, around the year 1490, also gave birth to the artistic movement known as Mannerism. As this style was a particularly important style in Spain, it has been given its own section below.
Mannerist Spanish Painting

Mannerism was a style that was developed principally in Italy, and especially Rome, by artists, sculptors and architects between 1510 and 1520. Mannerism was a particularly intellectual style of art and therefore appealed to people of the higher Spanish classes. However Mannerism was more exaggerated than previous styles, as Mannerist paintings were not as natural as the paintings from the earlier Renaissance period, seeking instead to be artificial and unstable.
There are many famous Mannerist artists, including Michelangelo who painted the ceiling of the Sistine Chapel in Italy. The most famous Spanish Mannerist painter was El Greco, who was in fact Greek.
El Greco has been adopted into the Spanish culture as he spent the majority of his life living and working in Toledo, Spain. Toledo was also the place where he produced his best works such as 'The Burial of the Count of Orgaz' (El entierro del Conde de Orgaz) and 'The Disrobing of Christ'(El Espolio).
Baroque Spanish Painting

Baroque art also originated in Rome, Italy and its development spanned two centuries, from 1590 until 1720. The Baroque style was present in painting, sculpture and architecture. Baroque art pieces were mostly commissioned by Catholic monarchs in order to enhance the assets of the expanding Catholic Church. Baroque art therefore also became a key part of the Counter-Reformation movement.
Baroque painting was designed to provoke some sort of emotion from the audience of the painting, unlike the rational paintings of the earlier Renaissance period. The most famous Baroque painter is of course, Carvaggio. However, Diego Velázquez is without doubt the best known Spanish painter of this style. Diego Velázquez was a Spanish painter who was active during the Spanish Golden Age period. Velázquez was a court painter and therefore painted many portraits of the Spanish Royal Family in Madrid, of which his most famous is the curious painting, 'Las Meninas'.
Romanticism Spanish Painting
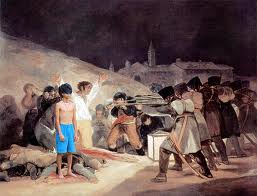
Romanticism became a fully developed art form by the end of the 18th Century. Romantic paintings incorporate elements of nature, heroism, humanity and emotions. Romanticism marked a movement away from the scientific approach to painting, towards a more expressive form. Romanticist paintings allowed the painter to be free with his painting and colours.
Romanticist painters also used their art to convey their feelings towards their own lives. Francisco Goya was the master of Spanish Romanticist painters. Goya produced several series of paintings, prints and engravings that conveyed his dark, twisted emotions.
Goya's 'Los desastres de la guerra' (The Disasters of War) were made as a protest against the violence during the uprising of the 2nd May 1808, or Dos de Mayo. 'The Black Paintings' (Las pinturas negras) were also an expression of Goya's dark inner feelings and troubles.
